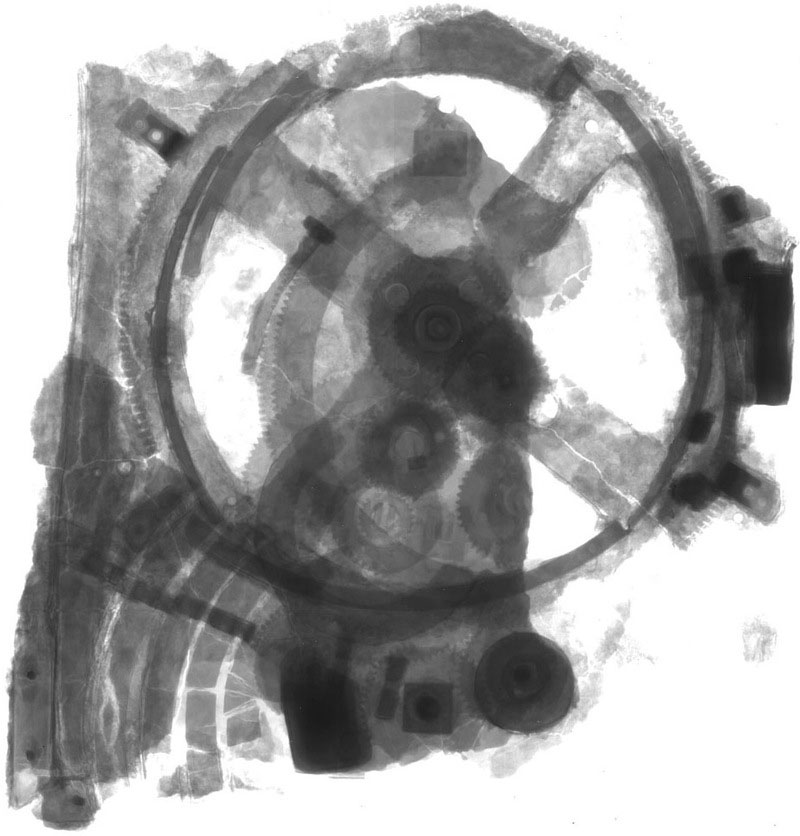
The Antikythera Device
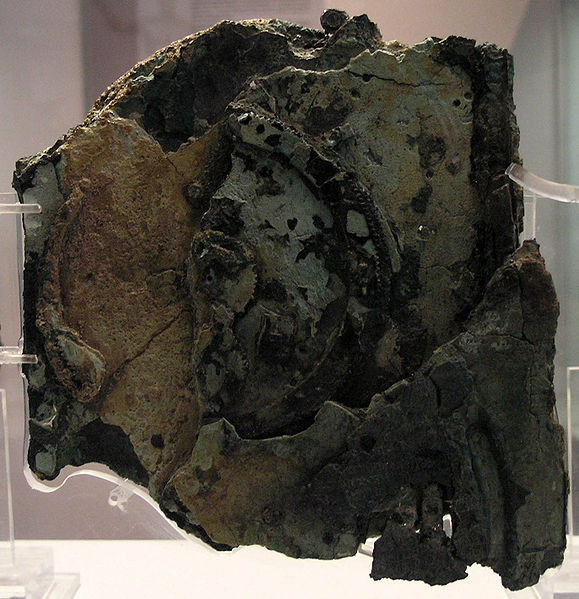
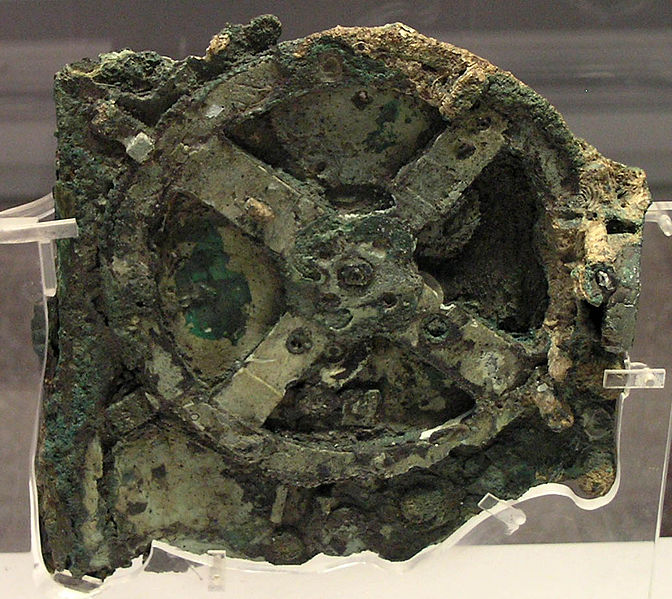
Discovered in a shipwreck off the Greek island of Antikythera in 1901, this collection of fused bronze gears and wood was originally thought to be a mechanical clock or astrolabe. Its function and complexity were not fully understood until it was examined with x-rays in 1974 when it was determined that the complex gearing could be used to track the rotation of the planets around the Earth (according to Ancient Greek understandings of Astronomy).
The shipwreck has since been dated to the first century BC.
The device is currently housed in the National Archaeological Museum, Athens.