Museum Sciences
It takes people from many different professions to make a museum successful. The Education Page is where you can find out about everything that goes on behind the scenes to make a museum run. How do we know what we know about the past? Where does an archaeologist begin?

Anthropology
Anthropology is the study of humankind both past and present that draws on social and biological sciences as well as the humantities and the natural sciences. In the united states, anthropology is typically divided into four subfields: socio-cultural anthropology, physical anthropology, archaeology, and linguitic anthropology

Archaeology
Archaeology is the study of human activity in the past, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and the environmental data that they have left behind. This typically includes the study of artifacts, architecture, biofacts, and cultural landscapes. Archaeologists study both human history and prehistory through a combination of survey, excavation and analysis of collected objects.
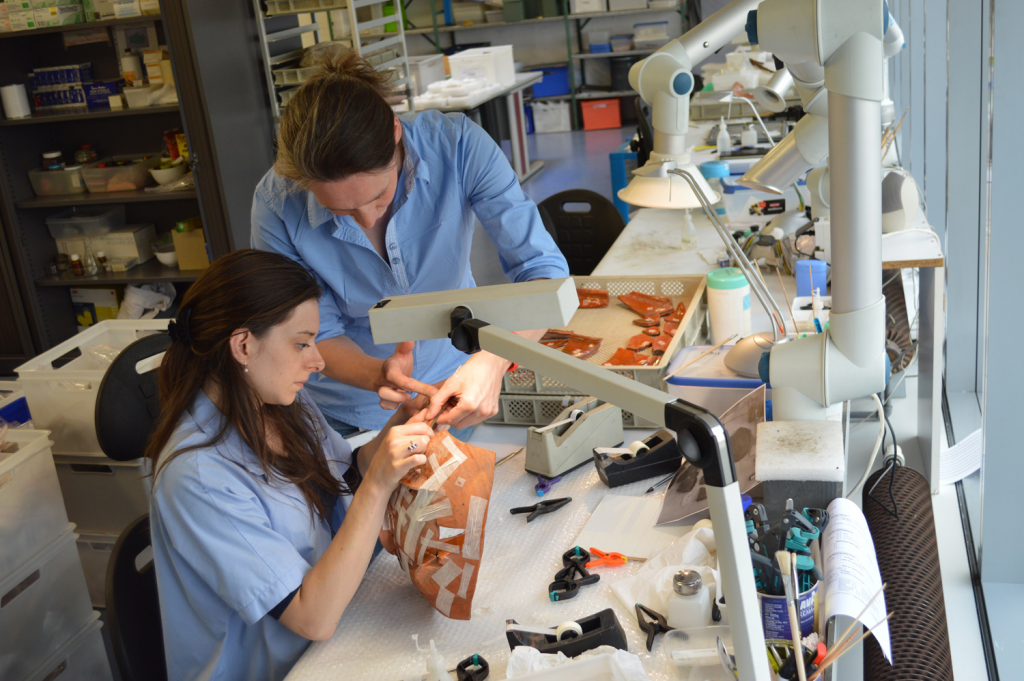

Conservation and Preservation
Conservation and preservation are often used interchangeably, particularly outside of the professional literature. Conservation, refers to the treatment and repair of individual items to slow decay or restore them to a usable state. Preservation is concerned with maintaining or restoring access to artifacts, documents and records through the study, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of decay and damage.

Curation
Curation is the process of selecting, organizing, maintaining and interpreting artifacts and objects in a museum’s collections. Curators are responsible for determining which items from a museum’s collections are put on display and helping to interpret their importance for visitors. A small museum may have only one curator who also acts as the administrator, while the largest may have dozens of curators, each overseeing different departments of the museum.
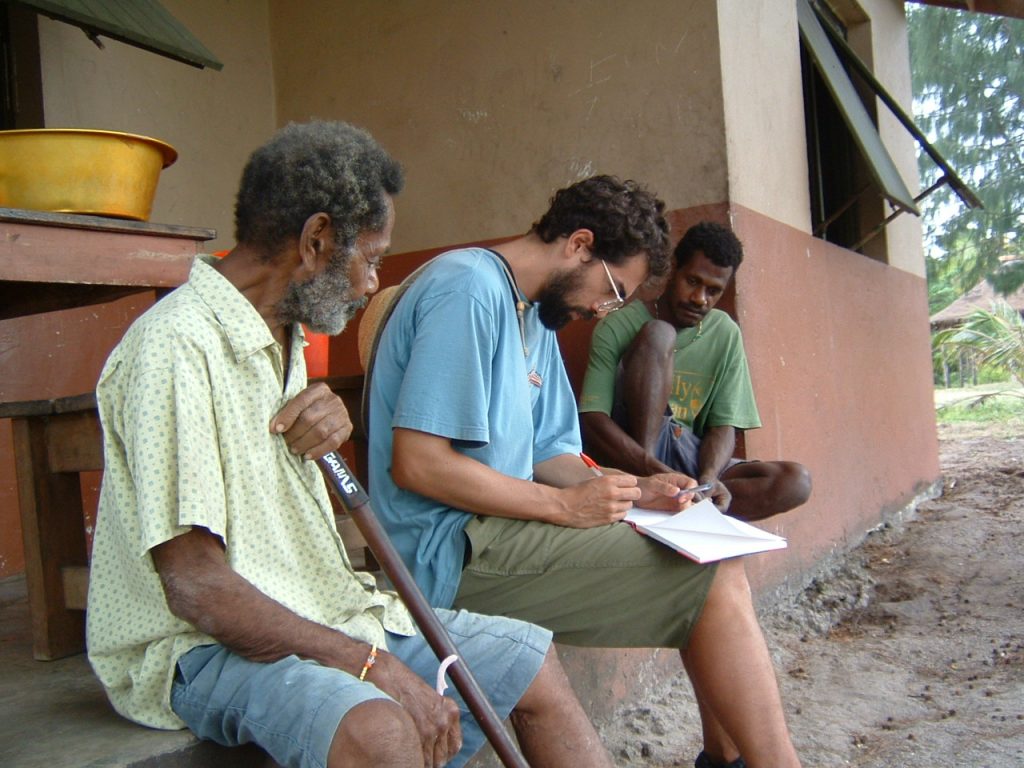

Ethnography
Ethnography is research designed to explore cultural phenomena, typically of living societies. An ethnography is a means to represent graphically and in writing the culture of a group. The resulting field study or a case report reflects the knowledge and the system of meanings in the lives of a cultural group.

Geology
Geology is the branch of Earth Science that deals with the rocks which form the earth and how they change over time. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks.

Historical Research
History is the study of the past, specifically how it relates to humans. It is an umbrella term that relates to past events as well as the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about these events. The term includes cosmic, geologic, and organic history, but is often generically implied to mean human history. Events occurring prior to written record are considered prehistory.

Paleontology
Paleontology is the scientific study of prehistoric life. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms’ evolution and interactions with each other and their environments. Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology (and draws on both disciplines), but it differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans.
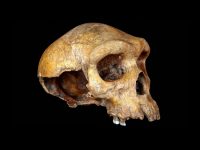
Physical Anthropology
Physical Anthropology is the study of human remains from the earliest hominids to anatomically modern humans. Physical anthropologists study the evolutionary process as it applies to humans, including their variability and adaptations too environmental stresses. They examine not only the physical form of their bones, but extrapolate the forms of muscles and organs and they they all function to allow survival of the species.
| Return to Education | Go to Becoming Human |
